There are multiple different peptides that modulate levels of growth hormone in your body. In this article we will cover peptides like Ipamorelin, Sermorelin, Hexarelin and of course, the king of them all, the Human Growth Hormone itself!

The Potency of Growth Hormone and Its Analogues
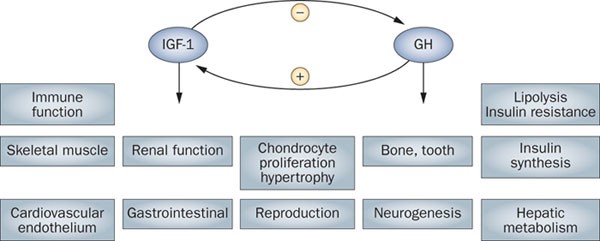
Growth Hormone (GH): Naturally produced by the pituitary gland, GH is highly potent due to its direct action on tissues to stimulate growth, metabolism, and cell regeneration. It influences various bodily functions including protein synthesis, muscle growth, and metabolism regulation. Its potency is also evident in its ability to significantly raise blood glucose levels by reducing the effectiveness of insulin, which can be both a therapeutic and a side effect, depending on the individual’s condition.
Hexarelin: Among the synthetic GH-releasing peptides, Hexarelin is noted for its strong efficacy in stimulating GH release. It is considered one of the most potent GH secretagogues available. This potency comes from its ability to rapidly increase levels of GH in the body, but it can also lead to increases in other hormones like cortisol, which may not be desirable depending on the user’s health goals.
Ipamorelin: Although slightly less potent than Hexarelin, Ipamorelin is effective in promoting GH release with a slower onset of action. Its appeal lies in its selectivity, primarily stimulating GH without significantly influencing other hormones such as cortisol or prolactin, which minimizes side effects and makes it suitable for longer-term use.
Sermorelin: As a GH-releasing hormone (GHRH) analog, Sermorelin is less potent compared to direct GH secretagogues like Hexarelin or even natural GH. However, its mechanism of action, which mimics the body’s natural signaling for GH release, offers a more controlled and gradual effect, reducing the risk of abrupt hormone fluctuations and associated side effects
Each of these agents has unique characteristics that can make it more suitable for certain users depending on their specific health needs, desired outcomes, and tolerance for side effects.
Specificity of Growth Hormone Peptides and Growth Hormone
Ipamorelin: Ipamorelin is highly specific in its action on stimulating growth hormone (GH) release, largely due to its targeted stimulation of the ghrelin receptor, also known as the growth hormone secretagogue receptor (GHSR).
This specificity allows Ipamorelin to trigger GH release without significantly impacting other hormones such as cortisol, prolactin, or ACTH, making it a favorable option for those seeking GH supplementation with minimal side effects. This targeted action aligns closely with the natural stimulation by growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), positioning Ipamorelin as a selective agent for clinical applications in GH therapies.
Sermorelin: Sermorelin acts primarily on the growth hormone-releasing hormone receptor (GHRHR) in the anterior pituitary gland. It mimics the action of natural GHRH, promoting the release of GH in a manner that preserves the body’s natural rhythms and feedback mechanisms.
This approach not only maintains normal pituitary function but also minimizes the risk of disrupting other hormonal pathways, making Sermorelin a specific and safer choice for long-term GH elevation. Its ability to improve GH levels while respecting the body’s intrinsic regulatory systems is particularly noted in its potential to enhance GH secretion without overexerting the gland’s capacity.
Growth Hormone (GH): As a therapy, exogenous GH directly supplements the body’s natural hormone, providing a specific and potent effect on growth and metabolic processes. However, this direct supplementation can also influence a broader range of systems beyond GH-targeted tissues, including potential impacts on glucose metabolism and insulin sensitivity due to its antagonistic actions against insulin. Therefore, while it is highly effective, it lacks the receptor-specificity that peptide secretagogues like Ipamorelin and Sermorelin offer.
Hexarelin: Hexarelin, although potent in stimulating GH release, exhibits less specificity compared to Ipamorelin and Sermorelin. It can influence other hormones such as cortisol and prolactin, potentially leading to broader systemic effects. This makes Hexarelin a less ideal choice for those seeking the specific benefits of GH increase without the accompanying hormonal fluctuations that can lead to side effects.
Side Effect Profile of Growth Peptides and Growth Hormone
Ipamorelin: Ipamorelin is generally considered to have the least side effects among growth hormone peptides due to its selectivity. The most common side effects are minor and include redness, itching, and pain at the injection site, along with dry mouth, nausea, and occasional headaches. These side effects are typically mild and manageable.
Sermorelin: Sermorelin is also well-tolerated, with the main side effects being localized reactions at the injection site, such as swelling, pain, or redness. These symptoms are usually short-lived and decrease with continued use as the body adjusts to the treatment.
Growth Hormone (GH):
Exogenous growth hormone can cause more significant side effects, particularly at higher doses. These include joint pain, insulin resistance, and fluid retention. Other potential side effects are increased blood glucose levels and possible contributions to long-term health issues if used inappropriately
Hexarelin: Hexarelin, while effective in increasing GH levels, has a broader range of side effects due to its potency and less selective mechanism. Common side effects include increased appetite, water retention, and potential tingling or numbness in the extremities. There are also concerns about the long-term effects on cortisol and prolactin levels, which could lead to more complex systemic effects.
Conclusion
In the comparison of growth hormone secretagogues—Ipamorelin, Sermorelin, Hexarelin—and Growth Hormone (GH) itself, several key factors such as potency, specificity, and side effect profiles stand out. GH is the most potent, directly enhancing growth and metabolic processes, but it may also affect a wide range of systems, potentially leading to side effects like joint pain and insulin resistance.
Hexarelin is quite potent among the peptides, yet its broader hormonal impacts may induce side effects such as increased cortisol and prolactin levels. On the other hand, Ipamorelin offers high specificity with minimal influence on other hormones, making it a preferred option for targeted GH stimulation with fewer side effects.
Sermorelin, while less potent, mimics natural hormonal pathways, thereby maintaining regulatory systems with minimal side effects, primarily at injection sites.
The choice between these treatments should consider individual health objectives, potential adverse effects, and personal health history, underlining the importance of professional healthcare advice for safe and effective use.