Both Enclomiphene and Clomiphene are medications used to address hormonal imbalances, particularly in men with low testosterone levels. While they share similarities, their differences can significantly impact their effectiveness and side effect profiles. Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision about treatment.
Understanding Clomiphene
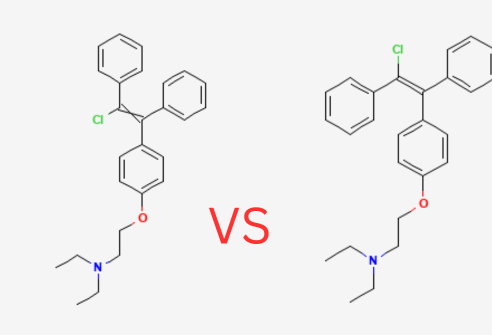
Clomiphene citrate is a selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) composed of two isomers: Enclomiphene (trans-isomer) and Zuclomiphene (cis-isomer). Clomiphene works by blocking estrogen receptors in the hypothalamus, stimulating the release of gonadotropins (LH and FSH), which in turn boost testosterone production.
Clinical Uses
Initially approved for treating female infertility, clomiphene has been increasingly used off-label in men to treat secondary hypogonadism and improve testosterone levels.
Potential Side Effects
Clomiphene’s side effects primarily stem from the presence of Zuclomiphene, which has estrogenic properties. Common side effects include mood swings, visual disturbances, and potential suppression of testosterone in some cases.
Understanding Enclomiphene
Enclomiphene is the purified trans-isomer of Clomiphene, meaning it acts as a pure estrogen antagonist. This selective action allows Enclomiphene to stimulate testosterone production without the estrogenic effects linked to Zuclomiphene.
Clinical Uses
Enclomiphene is primarily used to treat male hypogonadism and boost testosterone levels while maintaining sperm production.
Potential Side Effects
Compared to Clomiphene, Enclomiphene has fewer estrogen-related side effects. Patients using enclomiphene report lower instances of mood swings and visual disturbances.
Comparative Efficacy
| Factor | Enclomiphene | Clomiphene |
| Testosterone Levels | More targeted action, leading to a more predictable and stable increase in testosterone. | Increases testosterone but can have variable results due to the presence of zuclomiphene. |
| Spermatogenesis | Maintains sperm production more effectively as it lacks zuclomiphene. | Can impact sperm production due to estrogenic effects, leading to inconsistent outcomes. |
| Estrogenic Effects | No estrogenic activity, reducing risks of gynecomastia and mood swings. | Contains zuclomiphene, which can cause estrogenic side effects such as gynecomastia and mood swings. |
| Patient Tolerability | Generally well-tolerated due to its selective mechanism and lower side effect profile. | Higher risk of side effects due to mixed isomer composition, leading to more adverse reactions. |

Clinical Considerations
Treatment Selection
The choice between Enclomiphene and Clomiphene depends on the patient’s specific hormonal needs, medical history, and tolerance to side effects.
Monitoring and Follow-Up
Regular monitoring of hormone levels and symptoms is essential when using either medication. Blood tests should be conducted periodically to assess effectiveness and detect any adverse effects.
Conclusion
While both Enclomiphene and Clomiphene are effective in boosting testosterone levels, Enclomiphene offers a more targeted approach with fewer side effects. Consulting a healthcare provider, such as those at Empower Men’s Health Clinic, can help determine the most appropriate treatment for your individual needs.